Kryptops
| Kryptops Temporal range: Early Cretaceous, 110 Ma | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Reptilia |
| Clade: | Dinosauria |
| Order: | Saurischia |
| Suborder: | Theropoda |
| Family: | †Abelisauridae |
| Genus: | †Kryptops Sereno & Brusatte, 2008 |
| Type species | |
| †Kryptops palaios Sereno & Brusatte, 2008 | |
Kryptops (meaning "covered face", in reference to evidence that the face bore a tightly-adhering covering) is a genus of theropod dinosaur from the Early Cretaceous of Niger. It is known from a partial skeleton found at the Gadoufaoua locality in the western Ténéré Desert, in rocks of the Aptian-Albian age Elrhaz Formation. This dinosaur was described by Paul Sereno and Stephen Brusatte in 2008, with a single species to date: the type species K. palaios ("old").[1]
Discovery

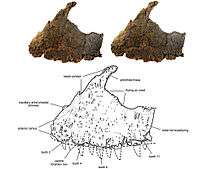
The holotype skeleton, MNN GAD1, includes a maxilla (main tooth-bearing bone of the upper jaw), vertebrae, ribs, and articulated pelvic girdle and sacrum, belonging to an adult about 6–7 m (20–23 ft).[1] According to the describers, this specimen represents one of the earliest known abelisaurids, and is notable for the heavily textured surface of the maxilla; the presence of pits and impressions of blood vessels indicates that there was a covering firmly attached to the face, perhaps of keratin. Sereno and Brusatte performed a cladistic analysis that found Kryptops to be the most basal abelisaurid. This was based on several features, including a maxilla textured externally by impressed vascular grooves and a narrow antorbital fossa, that clearly place Kryptops palaios within Abelisauridae as its oldest known member.[1] Carrano et al., on the other hand, consider Kryptops palaios to be a chimera, and state that its postcranial remains (especially a pelvis and sacrum), found some 15 metres from the holotypic maxilla, actually belong to a carcharodontosaurid (possibly to Eocarcharia dinops).[2]
See also
References
- 1 2 3 Sereno, Paul C.; Brusatte, Stephen L. (2008). "Basal abelisaurid and carcharodontosaurid theropods from the Lower Cretaceous Elrhaz Formation of Niger" (pdf). Acta Palaeontologica Polonica. 53 (1): 15–46. doi:10.4202/app.2008.0102.
- ↑ Carrano, Matthew T.; Roger B. J. Benson; Scott D. Sampson (2012). "The phylogeny of Tetanurae (Dinosauria: Theropoda)". Journal of Systematic Palaeontology. 10 (2): 211–300. doi:10.1080/14772019.2011.630927.